Here comes the first block of DxChain Storage testnet beta. After six months of design, development, and testing, DxChain officially launched the beta version of its data-side-chain test network last week, which realizes the blockchain storage capability DxChain has promised.

DxChain is a big data network dedicated to blockchain storage and computing. According to the DxChain’s roadmap, we plan to introduce the storage solution first and then come to the aspect of computing. This July, we officially released our Minimum Viable Product, which demonstrates some primary functions such as how to generate blockchains as well as upload and download files.
The testnet beta marks the beginning of DxChain’s productization. For example, the data side chain can enable transactions, file storage, and product scaling. We also released the DxChain browser, which allows users to see DxChain products visually.
Needless to say, the storage and computing capability are vital to the blockchain. Even the most successful blockchain applications Bitcoin and Ethereum are plagued with a limited amount of computation. Bitcoin is mainly used for financial transfer. Storage and computing are not involved. Ethereum demonstrates a step forward, but its amount of computation is still limited to only three million gas per block. The current smart contracts can execute some primary functions.
The blockchain technology today is mainly applied to money transfer and logistics. It encounters challenges to fulfill its potential and extend into new areas.
DxChain’s mission is to make blockchain function as a computing unit — storage and computing, so that the technical characteristics of blockchain can be truly extended to a broader field, promoting the next generation of technology from the bottom.
Here are the specific functions DxChain introduced in this release:
- Transaction function: the DxChain testnet beta can support the transaction in blockchain that lays the foundation for our economic model — encourage users to share available storage and computing power and uses tokens for payments & transactions. In the meantime, the file contract is also built on transactions. Today, we have developed a basic technological architecture for our file storage.
- File storage function: We implement the storage proof and Merkle Tree algorithm.
There is a storage proof process for users who want to share storage from their idle hard drives. Storage providers must prove that they indeed store files, and then users who are going to rent hard drives will make payments. We implement this feature in the testnet beta.
We apply the DxChain storage proof process by optimizing the Merkle trees algorithm. We designed a data structure that allows the verifier to complete the verification without having to own the original data file. The advantage of this algorithm is that it will verify a massive amount of files in a short time.
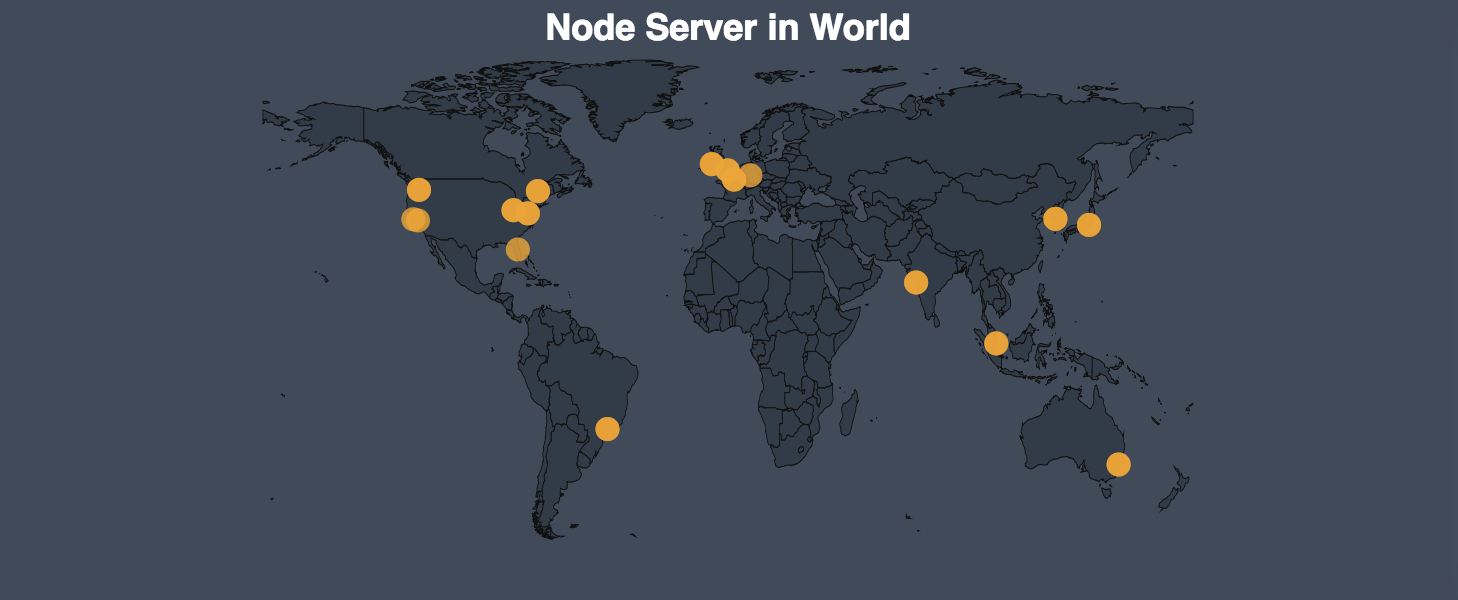
The Merkle Tree algorithm has been widely used in traditional CDs and DVDs in the past. In comparison to other algorithms, the Merkle Tree algorithm can reduce the redundancy of file copying while ensuring the file security. After encrypting a file, DxChain divides the file into several parts, and there is a partial duplication between each piece. For example, the file is divided into 30 pieces, and ten files contain all the original files. We can ensure the security of the original file as long as 10 of them exist. - Product scaling: In the last MVP, we used a small number of nodes to build a test network. In this testnet, we set up more nodes across five continents to verify the product performance in long distance. We have passed the test. The number of nodes can be arbitrarily increased in the future, which means that DxChain can scale our products.
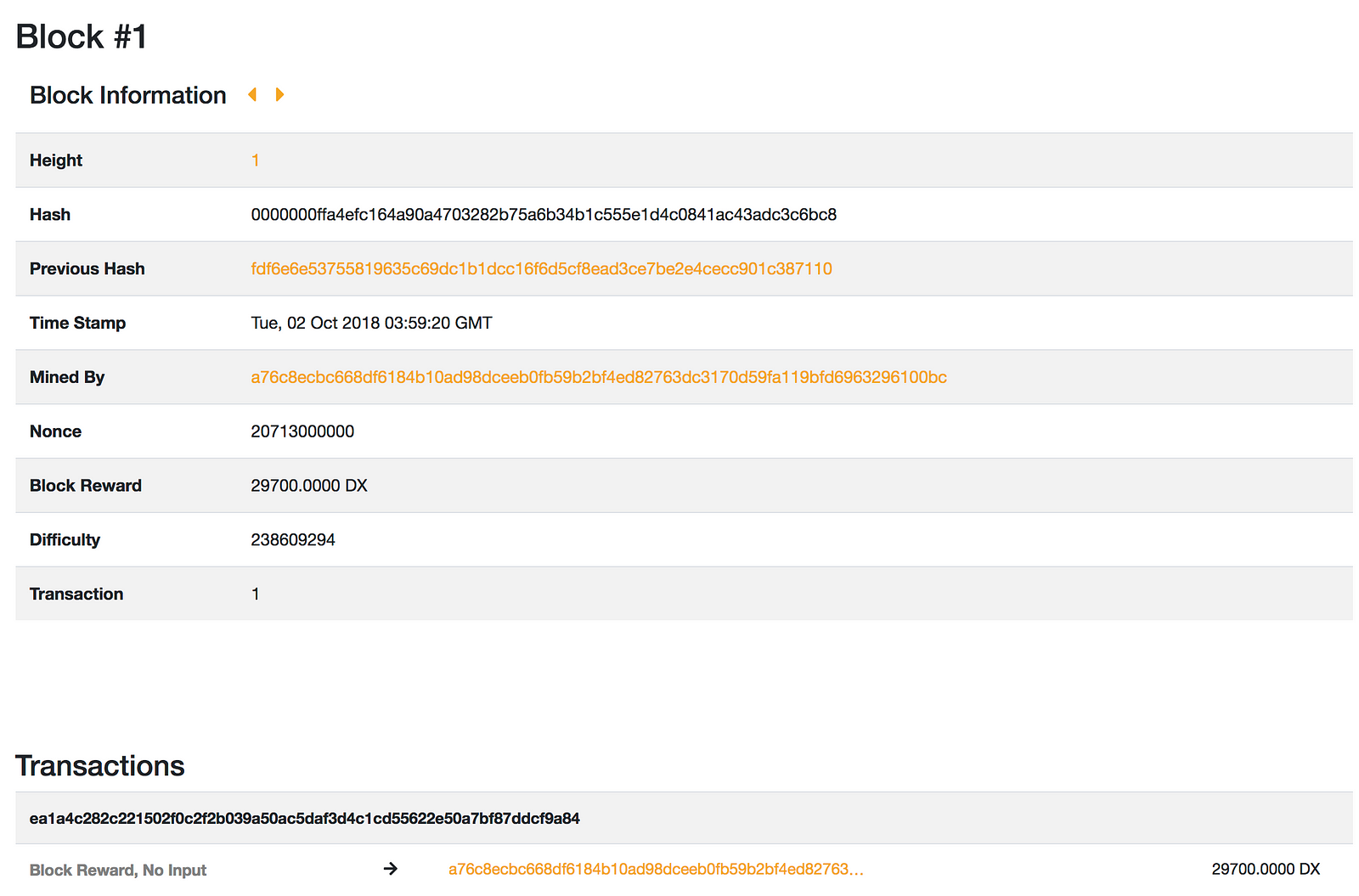
- The block browser supports the following information of: The DxChain product, which includes blocks, addresses, transactions, and nodes.
Next, we will release the official version of the testnet and mainnet in the fourth quarter. Most useful features will be available by the end of this year.
DxChain uses “chains-on-chain” architecture to address the issues of data storage, computation, and privacy. The architecture includes a master chain, a data chain, and a computation chain. The computing chain is used for parallel computing applications to process large volumes of data, which eventually powers machine learning and business intelligence. The data chain is used for data storage, privacy protection, and support for the computing chain. The master chain is used for operating blockchain transactions while coordinating the computation and data chains.
Also unique is our Hadoop-style architecture. Over the past decade, Hadoop has addressed the issue of distributed data storage within an organization or a company. However, the problems of how to achieve trust between different organizations and participants to make distributed storage remain unsolved.
We integrate Hadoop’s forte, which has been validated in industries over the past decade, with blockchain’s unique mechanism to eventually solve the problems of distributed storage and computing in a decentralized environment.
We hope our public chain will become a distributed Hadoop at the age of blockchain — providing the most stable and universal decentralized storage and computation solution.
